Explain Stages of Renal Disease
No healthway post selected for this post.
What is renal disease?
Our kidneys perform very important functions. Some of ways kidneys keep our all body in balance by:
-
Removing extra water and waste products from our body
-
Helping in formulation of red blood cells
-
Balancing vital minerals in our body
-
Maintaining our blood pressure
-
Keeping our bones healthy
Chronic renal disease is when the kidneys become damaged with the passage of time (for at least 3 months) and have difficulty in performing all the above functions. Renal diseases also increase the risk of many other health issues such as stroke and heart disease. Developing renal disease is generally a slow process with few symptoms at first. So, chronic renal disease is commonly divided into 5 stages to make treatment easy.
In this article, we will discuss 5 stages of renal disease in detail.
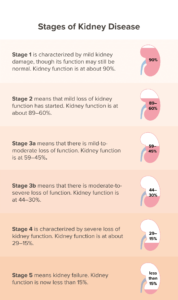
Stages of renal disease
Renal disease is commonly evaluated by using two simple tests:
-
A blood test named as the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
-
A urine test referred as urine albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR)
Both of these tests help to determine the functioning of the kidney. When indicating the stage of renal disease, these tests commonly need to be repeated continuously to confirm any long-term damage.
Stage 1 renal disease
eGFR 90 or may be higher and some kidney damage (such as uACR 30 or higher) for about 3 months or more
Stage 2 renal disease
eGFR 60-89 and mild kidney damage (such as uACR 30 or may be higher) for 3 months or more
Stage 3a renal disease
Mild to moderate loss of functioning of kidney (eGFR around 45-59 for 3 months or more)
Stage 3b renal disease
Moderate to severe loss of kidney functioning (eGFR about 30-44 for 3 months or more)
Stage 4 renal disease
Severe loss of kidney functioning (eGFR 15-29 for about 3 months or more)
Stage 5 renal disease
Kidney failure (eGFR less than 15 for about 3 months or more)
or you may need dialysis to survive
Stage 1 renal disease
In stage 1 renal disease, there is slight damage to kidneys. They are flexible and can perform 90% or better functioning.
At stage 1, renal disease is probable to be discovered by routine urine and blood tests. You may also need these tests if you have high blood pressure or diabetes, the leading causes of renal disease in the United States.
Symptoms
Usually, there are no symptoms when your kidneys function about 90% or more.
Treatment
You may slow disease progression by adopting these steps:
-
Manage blood sugar levels if you are diabetic.
-
Listen to the advice of your doctor if you have hypertension to control your blood pressure.
-
Maintain a balanced, healthy, diet.
-
Avoid tobacco.
-
Perform physical activity for 30 minutes daily, at every cost 5 days a week.
-
Maintain a healthy weight according to your height.
Ask your doctor to refer you to a kidney specialist (nephrologist) if you do not see a kidney specialist.
Stage 2 renal disease
In stage 2 renal disease, your kidney functions between 60-89%.
Symptoms
At this stage, you still can be symptom-free. Or symptoms are general, such as:
-
fatigue
-
itching
-
loss of appetite
-
sleep issues
-
weakness
Treatment
There is no cure for chronic renal disease, but treatment at stage can slow progression.
It’s necessary to treat the underlying cause. If you have high blood pressure, diabetes, or heart disease, follow the advice of your doctor to manage these issues.
It’s also necessary to exercise regularly, maintain a good diet, and manage weight. You should stop smoking, if you smoke.
Stage 3 renal disease
Stage 3A renal disease means that your kidney functioning is between 45-59%. Stage 3B renal disease means your kidney functioning is between 30-44%.
The kidneys are unable to filter fluids, toxins, waste, well, so they start to build up.
Symptoms of stage 3 renal disease
Not every person faces symptoms at stage 3 kidney disease. But a person may feel:
-
back pain
-
fatigue
-
loss of appetite
-
continuousitching
-
sleep problems
-
swelling of feet and hands
-
frequent urination of less production of urine
-
weakness
Complications generally include:
-
anemia
-
high blood pressure
-
bone disease
Treatment
It’s necessary to manage underlying health conditions to help manage kidney function. This commonly include:
-
medications for high blood pressure such as angiotensin II receptor blockers or angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
-
low-salt diet and diuretics to sooth fluid retention
-
cholesterol-lowering medicines
-
erythropoietin supplements to treat anemia
-
treatment of weakening bones by vitamin D supplements
-
phosphate binders to avoid calcification in blood vessels
-
follow a low-protein diet so that your kidneys don’t need to work as hard
You’ll likely need continuous follow-up tests and visits.
Your doctor will refer you to a dietitian to make sure you get all the essential nutrients.
Stage 4 renal disease
Stage 4 renal disease means you have moderate-to-severe damage to the kidney. Kidneys function between 15-29%, so a person may build up more fluids, toxins, and waste, in your body.
You should take all the necessary steps you can to prevent progress to kidney failure.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC), about 40% of people having severely reduced kidney functioning aren’t even know they have this issue.
Symptoms
Symptoms usually include:
-
back pain
-
chest pain
-
reduction in mental sharpness
-
fatigue
-
loss of appetite
-
muscle cramps or twitches
-
nausea and vomiting
-
constant itching
-
shortness of breath
-
sleep issues
-
swelling of hands and feet
-
frequent urinationor less urine production
-
weakness
Complications may include:
-
anemia
-
high blood pressure
-
bone disease
You may also have a higher risk of stroke and heart disease.
Treatment
In stage 4 renal disease, you should work closely with your physicians. Besides, same treatment as early stages, you must start conversations about kidney transplant and dialysis.
These procedures take a lot of time and careful organization, so it’s sensible to start planning for these processes with your doctor as soon as possible.
Additionally, stage 4 renal disease may lead to further health complications. For example, it is rare for people to progress metabolic acidosis due to renal disease. Depending on the blood bicarbonate levels, your doctors usually prescribe oral bicarbonate replacement therapy.
Stage 5 renal disease
Stage 5 renal disease means your kidneys work less than 15%, or you may have kidney failure.
When this happens, the buildup of toxins and waste becomes life threatening. This is the end-stage or last-stage renal disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms of kidney failure may include:
-
chest and back pain
-
breathing issues
-
decrease mental sharpness
-
fatigue
-
little or no appetite
-
muscle cramps or twitches
-
nausea and vomiting
-
urination problems
A major drop in the functioning of kidney puts more stress on the heart, increasing risk of stroke and heart disease.
Treatment
Once you have kidney failure, then life expectancy is only some months without kidney transplant or dialysis.
Dialysis is not a cure for renal disease but this process removes fluids and waste from your blood. There are two types of dialysis:
-
hemodialysis
-
peritoneal dialysis.
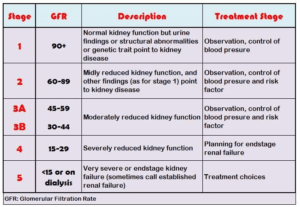
Chronic renal disease stages chart
| Stage | GFR | Percentage of kidney function | Description |
| 1 | >90 mL/min | >90% | Normal to high kidney function |
| 2 | 60–89 mL/min | 60–89% | Mild decrease in function of kidney |
| 3A | 45–59 mL/min | 45–59% | Mild to moderate decrease in kidney function |
| 3B | 30–44 mL/min | 30–44% | Mild to moderate decrease in kidney function |
| 4 | 15–29 mL/min | 15–29% | Severe decrease in functioning of kidney |
| 5 | <15 mL/min | <15% | Kidney failure |
Frequently asked questions
Is renal failure a stage of death?
Stage 5 is the most dangerous stage of renal disease and kidney function commonly below 15%.
What is creatinine level for stage 3 renal disease?
The creatinine level for stage 3 kidney disease in older adults were:
-
For men: below or equals to 1.3 mg/dl
-
For women: below or equals to 1.0 mg/dl
This creatinine level is regardless of absence or presence of diabetes, hypertension, or congestive heart failure.
How much time does it take to go from stage 3-stage 4 renal disease?
About half patients with stage 3 renal disease progressed to the stage 4 or 5 over 10 years.
What is the life expectancy of stage 3 renal disease?
The average life expectancy of stage 3 kidney disease is 24 years in women who are 28 and 40 in men.
What is creatinine level for stage 4 renal disease?
The creatinine level for stage 4 kidney disease is 15-29 mL/min (GFR).
Summary
Kidney removes wastes and toxins from our body. Sometimes, the kidney cannot remove waste perfectly. At this point, toxins build-up in our body and cause diseases. There are 5 major stages of renal diseases. At an early stage we can treat this disease, but in later stages we can only slow down the progression of renal disease.
No healthway post selected for this post.
